February 2025
Single-cell sequencing made simple
Introducing Illumina Single Cell 3’ RNA Prep, a highly efficient, affordable, and accurate workflow for single-cell analysis. Accessible for more labs with an easy, scalable, and microfluidics-free workflow, researchers can now undertake larger and more varied multiomic studies to scale experiments from hundreds to millions of cells.






Did you know?
Give me details
What method combines CRISPR-based genetic screening with single-cell RNA-sequencing?
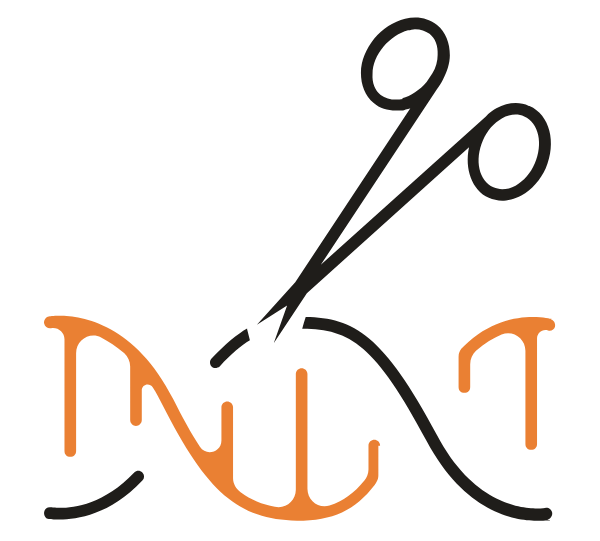
The Perturb-Seq method uses single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq) for CRISPR-based screens yielding information-rich readouts, which can be used to dissect complex cellular pathways and develop maps of gene and cellular function.
Read the technical note, written in collaboration with Single Cell Discoveries, for an overview of genome-wide Perturb-Seq on the NovaSeq™ X Series.
What is the name of the Illumina technology, which eliminates the library preparation step in the sequencing workflow?
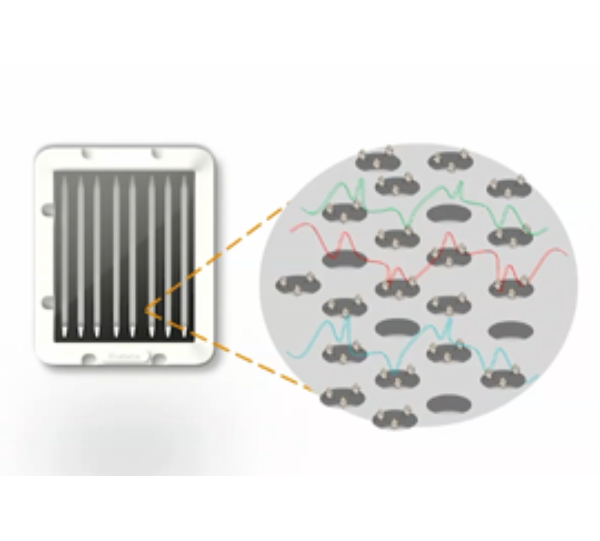
Introducing constellation mapped read technology, a highly simplified NGS workflow that enables on-flow-cell library prep that eliminates the standard library prep step prior to sequencing.
To learn more, read the article describing constellation.
Innovations to enable multiomics
Powering therapy research with single-cell sequencing
[Video] The team at Single Cell Discoveries (SCD) in Utrecht, the Netherlands, revolutionized their workflow to run projects with millions of cells in a single experiment. Watch this video to see how SCD is leveraging the speed and scale of their NovaSeq X Plus combined with their expertise in single-cell technologies to deliver fast and impactful results for their customers.
79-gene panel for detection of low-frequency variants in liquid biopsy samples
[Application Note] The custom predesigned panel using Illumina Cell-Free DNA Prep with Enrichment enables low-frequency variant detection in tumor samples across 79 genes. Improved laboratory efficiency by performing a single workflow for both tissue and liquid biopsy samples.
Multiomics in action
Publication highlights from the research community
Liquid Biopsy
Single-cell/Spatial
Microbiomics
Digoxin for reduction of circulating tumor cell cluster size in metastatic breast cancer: a proof-of-concept trial
This study, by Nicola Aceto's team in Zurich, illustrates a great approach to better understand the role of metastasis in cancer-related death. Compared to individual circulating tumor cells (CTCs), CTC clusters demonstrate higher metastatic potential and thus significant impact on cancer progression. In this publication, the effect of Na+/K+ ATPase digoxin was evaluated in a proof-of-concept study in women with metastatic breast cancer. Results showed CTC cluster size reduction, while CTC transcriptome profiling revealed downregulation of specific genes upon treatment with digoxin.
Learn more about the Illumina portfolio for analyzing liquid biopsy samples.
Liquid Biopsy
Single-cell/Spatial
Microbiomics
An organotypic atlas of human vascular cells
This publication represents an enormous collaborative effort to generate an integrated multi-organ human vascular cell atlas. From 19 organs and tissues, the research teams were able to identify 42 vascular populations with shared and tissue-specific features. The research teams created a comprehensive open-access vascular cell atlas to serve as a valuable resource for understanding vascular cell diversity, functional roles, and implications in diseases which can inform future studies and therapeutic targeting in various vascular-related disorders.
Watch Ana-Maria Cujba (Wellcome Sanger Institute) presentation on Human Cell Atlas.
Liquid Biopsy
Single-cell/Spatial
Microbiomics
Host-microbe multi-omics and succinotype profiling have prognostic value for future relapse in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
Researchers from University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, together with their collaborators, investigated the potential of using comprehensive host-microbe multiomic analyses from mucosal biopsies to predict relapse in individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). By integrating various omics data from host (transcriptomics and methylation analysis) and gut microbiome (16S profiling and gene expression patterns), they aimed to identify biomarkers or signatures that may enhance personalized treatment strategies and improve disease management for IBD patients.
Learn about Illumina Infinium® HumanMethylation EPIC array.
