July 2025
Illumina Epigenetics Research Grant Contest
Applications for the 2025 Illumina Epigenetics Research Grant Contest are open. Deadline for all submissions is 24 August 2025. Eligible applicants are invited to submit an abstract describing a new project using Infinium™ Methylation Screening Array-48 Kit. One winner will be selected from all qualified applications by a panel of experts to win the award valued at over $100,000 USD.






Did you know?
Give me details
It’s really simple. Partek™ Flow™ streamlines methylation array data analysis.
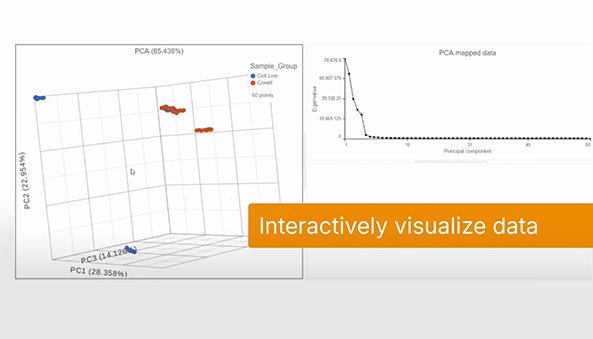
Interactive data visualization, powerful statistics, and comprehensive analysis of methylation array data. Build heat maps in a few clicks, it’s really that simple. Learn about Partek Flow data analysis solution.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) and protein detection are coming together to enable multiomics-based understanding of health and disease.
Proteomics Partnerships Move Multiomics from Theory to Practice
Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News recently interviewed executives across the industry, including Fiona Kaper and Dalia Daujotyte, leaders of the proteomics strategy at Illumina. Read about Illumina Protein Prep solution that is helping to bring scalable, high-fidelity protein discovery to researchers everywhere.
Innovations to enable multiomics
Illumina Connected Insights: A Turning Point In Oncology Genomics
Illumina Connected Insights (ICI) software harnesses extensive knowledge sources via powerful API-integrations for streamlined variant interpretation, including prioritization of relevant clinical trials, drug labels, and guidelines for clinical research. Hear more details on ICI in the Mendelspod podcast interview with Jing Gao, VP of Software Engineering at Illumina.
AI Tool Identifies Disease-Driving Promoter Mutations
Using genomic data from tens of thousands of individuals, scientists at Illumina have developed a deep neural network that can predict how changes in promoter sequences will affect gene expression. Published in Science, the PromoterAI tool accurately identifies promoter variants that dysregulate gene expression. More details in this interview with Kyle Farh, Vice President at Illumina Artificial Intelligence Lab.
Multiomics in action
Publication highlights from the research community
Bioinformatics
Epigenomics
Genomics
Predicting expression-altering promoter mutations with deep learning
Published in Science, this paper describes PromoterAI, a new tool from the team at Illumina Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. It’s a deep learning algorithm that identifies potential disease-causing variants within “promoter” sequences in the human genome. This algorithm will empower clinical researchers to better understand the causes of rare genetic diseases and cancer, and drive the discovery of novel therapeutic targets in biobank-scale cohorts.
Learn more about PromoterAI
Bioinformatics
Epigenomics
Genomics
Clonal tracing with somatic epimutations reveals dynamics of blood ageing
In this study published in Nature, researchers in Spain and Germany used targeted single-cell methylome sequencing analysis to map DNA methylation at CpG sites across the genome in hematopoietic cells in mice and primary human bone marrow samples. Their results identified stochastic DNA methylation changes that provide insights enabling identification of age-related expansions in clonal cell populations, indicating the need for further investigation of age-related decline in clonality.
Learn more about solutions for DNA methylation
Bioinformatics
Epigenomics
Genomics
Predicting resistance to chemotherapy using chromosomal instability signatures
Research teams from UK and Spain collaborated to develop chromosomal instability (CIN) signatures which could potentially be used to guide selection of chemotherapy. Using these CIN signatures, tumors with resistance to these cytotoxic agents could be identified allowing for selection of an alternative therapy. In this paper, the authors show feasibility of using CIN signatures as biomarkers on targeted-capture gene panel sequencing of tumor combined with shallow whole-genome sequencing (sWGS) of plasma showing promise to advance precision use of cytotoxics and improve overall health outcomes.
Learn more about next-generation sequencing solutions for genomic profiling

Educational resources to learn more
Understanding DNA methylation and its applications for human disease research
Understanding DNA methylation and its applications for human disease research
This eBook covers DNA methylation and its applications in the study of human diseases and other phenotypes. It covers epigenome-wide association studies (EWAS), including considerations for study design, sample types, and data analysis.